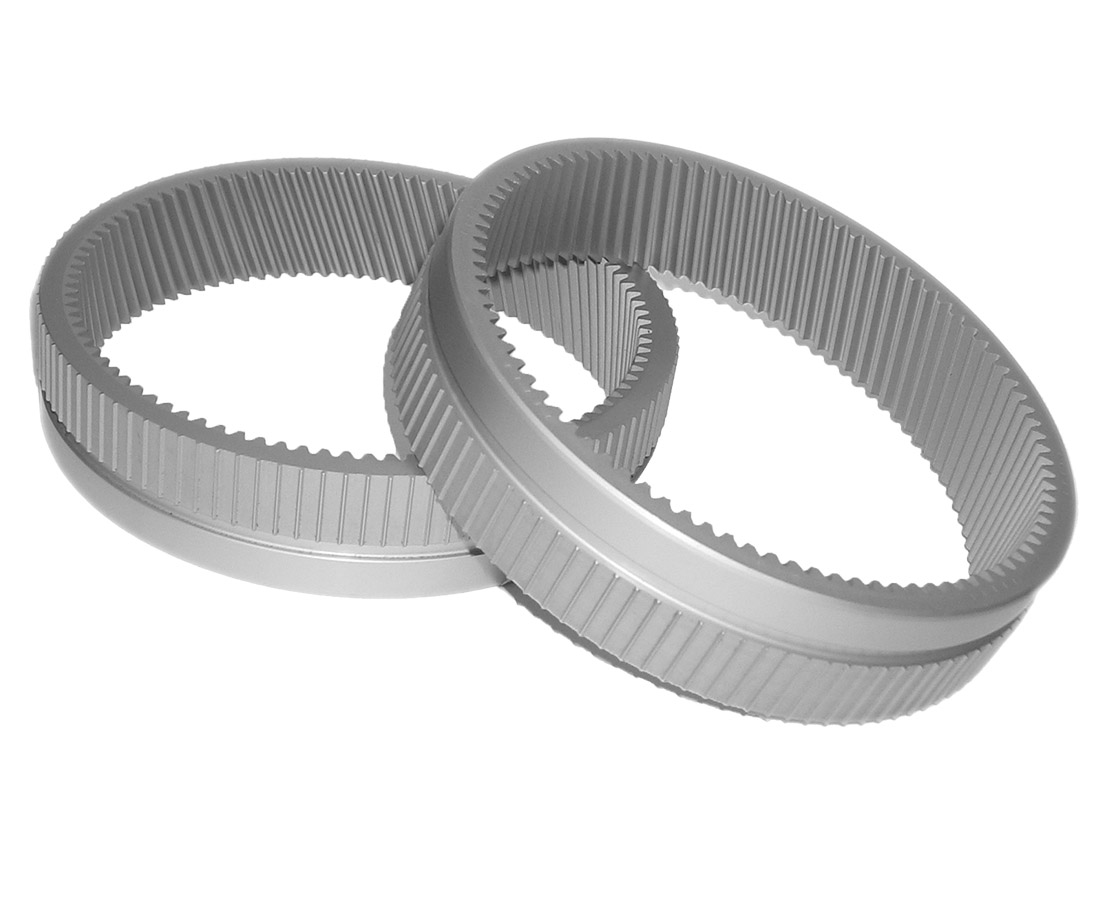
Nitrex Turnkey Systems & Technologies
Nitrex nitriding / nitrocarburizing systems and technologies deliver superior quality and reliability year after year while optimizing the performance and cost efficiency of the application.
HT services
NITREG®-C CONTROLLED NITROCARURIZING
UPC Upgrades
UPC-Marathon control upgrade solutions are modular in design to improve nitriding/nitrocarburizing operations,
meet industry standards requirements, and ultimately provide precise and reliable process control.